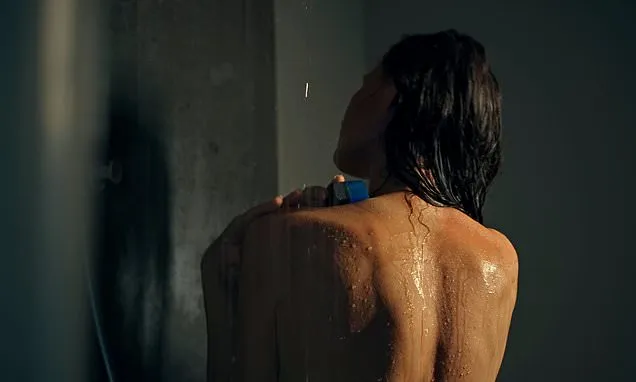If you struggle to fall asleep at night, taking a shower in the dark could be the key to a full night's rest.
While sleep scientists have long advised avoiding screens before bed, experts have now backed a viral social media trend, which may improve sleep quality.
Poor sleep has been linked to multiple serious health problems, including cancer, stroke and infertility.
The 'dark showering' trend is as simple as it sounds, involving switching off the bathroom light before stepping into the shower.
The practice has been popular among wellness experts for years, who claim the practice is a way to 'cleanse the energetic residue of the day and prepare for night, rest or intimacy'.
In recent months, however, it has also gained traction online with social media users raving over its benefits.
One recent video is captioned: 'Here is your sign to take a dark shower after a long day behind blue lights to regulate your nervous system and sleep like a baby.'
While there is little research on dark showering as a standalone sleep technique, sleep science is clear that bright light in the evening can signal to the brain's internal body clock that it is still daytime.
This delays the release of melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate sleep and is often described as the body's 'darkness signal'.
In a sense, light acts as a 'cup of coffee' for the brain, which is why experts recommend dimming lights in the evening to keep the body clock aligned.
Bathrooms are often the brightest rooms in a home, designed to be helpful for daily routines such as grooming, applying makeup and shaving.
In many modern flats, bathrooms lack windows, meaning that intense artificial lighting is required to make the space feel open, airy and inviting rather than enclosed and dark.
But in the evening, these lights can send a strong signal that it is still daytime.
In one study, volunteers were exposed to standard bathroom lighting for just 30 minutes at bedtime.
Melatonin levels dropped, and the volunteers' self-reported alertness increased, even though participants remained in the bathroom.
Another study of adolescents found that a burst of bright light in the early evening reduced melatonin levels three hours later and delayed the normal rise in sleepiness.
Many people prefer to shower or bathe in the evening as it can make them feel more relaxed.
And there is scientific evidence showing that nighttime showers fall asleep faster than those who shower in the morning.
A 2019 study found that a warm bath or shower an hour or two before bedtime can help you unwind and fall asleep faster because it will help lower your core temperature.
Warm water widens blood vessels in the hands and feet, helping core body temperature drop afterwards, a key signal for drowsiness.
Showing in the dark may also help prepare the nervous system for sleep.
Low light reduces the brain's alerting signals and makes it easier to shift from a state of vigilance, often called the 'fight or flight' response, into a calmer 'rest and digest' state.
While no large trial has directly compared dark showers with brightly lit showers while measuring objective sleep outcomes, the trend has proved to be effective for many people.
Dr Clare Rooms, clinical lead for Insomnia at Boots Online Doctor, previously said that while showers in low light won't solve severe or persistent sleep issues on their own, they 'can be a helpful part of a relaxing pre-bed routine'.
The 'dark showering' trend also aligns with a broader Gen Z preference for ambient, cosy lighting over harsh overhead lighting.
It complements the popular 'everything shower' trend, transforming a daily routine into a self-care ritual.
Those with mobility issues should be careful about trying this trend, as it can create a trip hazard.